Technology nuggets and resources to drive your innovation
Boost your innovation with fusion tech
SELFIE : superconducting joint test facility
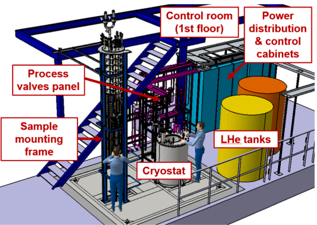
CEA designed and built a superconducting joint test facility called SELFIE. The test performed on SELFIE aims to measure the superconducting joints sample resistance (few nΩ) in cryogenic condition (liquid helium bath at 4.2 K) at 70kA in self-field. This system is designed to perform easily and in a more efficient way. This facility has already been declared ready for operation in January 2022. Furthermore, the SELFIE facility is also available for other superconductivity materials
Double acting linear actuator without friction and lubrification for harsh environment
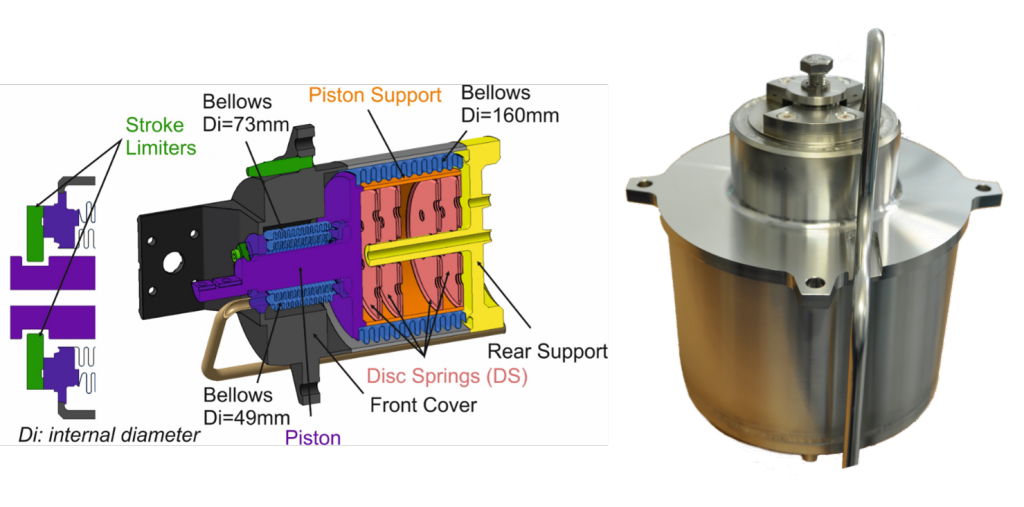
Scientists of Forschungszentrum Jülich have developed an innovative actuator concept offering double-acting linear movement without friction and without lubrication. This technology is particularly suitable for use in extreme environments and has been implemented as a linear motor for a shutter and as a linear drive for a sensor in an ITER experiment. The linear drive can be used as a servomotor for an orifice plate / shutter release or as drive mechanism for a sensor movement and could be suitable for use with different fluids, i.e. gases or even liquids in many industrial applications.
Gamma spectrometry for radioactive material characterization
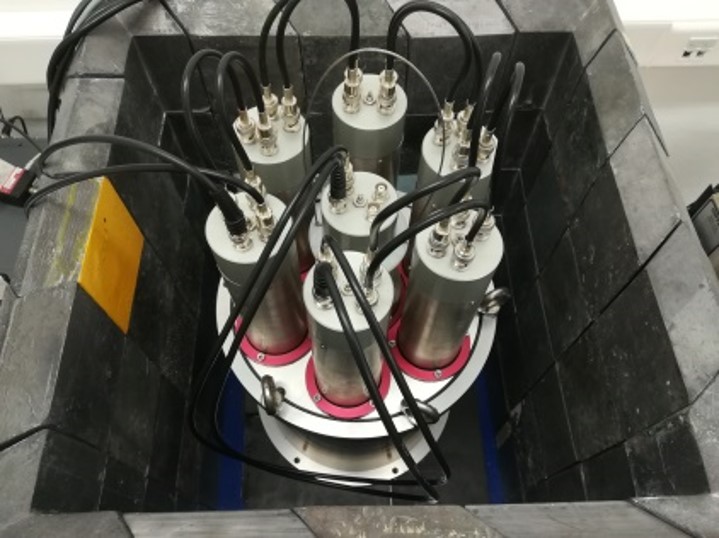

The National Center for Scientific Research “Demokritos” (CNRD) has developed specific facilities and methodology for the radiological characterization of nuclear materials! Indeed, nuclear fusion research requires the investigation of the radiological properties of ITER material samples after neutron irradiation, the validation of neutron streaming and material activation calculations at positions close and far from the plasma source and finally the development of a new activation detector for neutron fluence measurements and spectrum evaluation in the breeding blanket of future fusion power plants. Radiation measurements of materials, in conjunction to radiation transport simulations, are available at their lab for use in nuclear, environmental, industrial and medical applications, where accurate non-destructive measurements of radioactivity in samples of up to several liters in volume are required.
Ionizing and not-ionizing radiation for studies on materials and devices
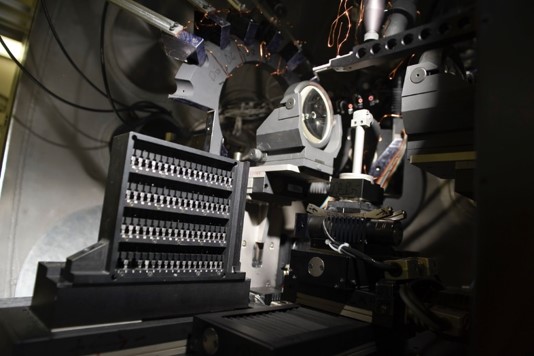
Operated at ENEA-Centro Ricerche Frascati for inertial fusion research, ABC laser provides the most energetic laser pulse in Italy. It can deliver two infrared laser beams that, when interact with suitable targets generate intense ionizing and non-ionizing radiations. These can be used to study the response of specific materials and devices to pressures, electromagnetic and particle radiation stresses produced by the interaction, that become as a point-like compact intense radiation source, unavailable with other methods. The fields of application mainly regard nuclear fusion, particle acceleration, space applications, material science, radiation hardness of devices and materials, medical and biological studies.
Structural, Mechanical and Physical Properties Characterization facility for High Performance Materials

National Centre for Scientific Research “Demokritos” gained extensive know-how and capabilities on multi-purpose characterization of high-performance materials for extreme environments supporting material optimization in the intended application and overall performance improvement. The facilities and know-how have been generated for the characterization and development of fusion structural, high heat flux and functional materials, allowing for dozens of material properties to be accurately determined. Thanks to these remarkable performances, preliminary applications for materials used in aerospace applications have already been found. Material characterization in conjunction with know-how for innovative material development and material testing capabilities are now available for further use in applications where materials are exposed to extreme environments, like Nuclear, Aerospace, Energy systems, Automotive, Marine and Defence sectors.
Investigating radiation damage in materials using ion beam
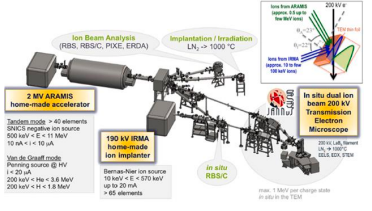
Considering the evolution of microstructures and material properties under extreme radiation conditions, the JANNuS facility has been developed at University Paris-Saclay that allow multi-scale modelling of radiation effects in materials with in situ observations of microstructure modifications. The versatility of conditions in terms of particle energy, dose rate, fluence, etc., is a key asset of ion beams allowing fully instrumented analytical studies. Coupling of two or more beams, use of heated/cooled sample holders, and implementation of in situ characterization and microscopy pave the way to real time observation of microstructural and property evolution in various extreme radiation conditions more closely mimicking the nuclearenvironments.
Many promising applications in electronics, space, geologyare considered.
Optimum grating parameters for a VUV (vacuum ultraviolet) spectrometer

The object of the invention is to provide manufacturing parameters for a holographic diffraction grating on a concave or toroidal surface, which is used as the single optical element in a VUV spectrometer with a flat detector. The spectrometer geometry is also defined alongside the diffraction grating parameters. The invention from the research center Juelich (Germany) consists of a proprietary software code which uses various numerical methods to determine the optimal grating parameters, with the aim of producing such gratings for VUV spectrometers with a minimal line width for a pre-‐defined wavelength and at the same time achieving high spectrometer efficiencies.
Ultra Sniffer New leak detection method

The test sensitivity of classic sniffer test methods is limited by the helium concentration in the air, but by reducing the atmospheric helium concentration the test sensitivity can be significantly improved. The Ultra Sniffer Test gas (UST) method is simple – there is no evacuation of the test chamber, only a filling with helium free gas. The method has successfully been used for testing super conducting coils for Wendelstein 7-‐X at the Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics (IPP) in Greifswald. The technology is ready for use in the non-‐fusion domain and is currently being commercialized by the inventor, Mr. Robert Brockmann.
MANTIS: a real-time quantitative multispectral imaging system

MANTIS is a multispectral imagining system, based on a new diagnostic technique recently developed in a collaboration between MIT-PSFC, EPFL, and DIFFER and used to monitor the discharges in the fusion experiment (TCV’s system and MAST-U). The MANTIS system collects light through a single window in the tokamak and feeds it to ten cameras that each look at a very narrow wavelength band. MANTIS can analyse density, temperature and the presence of impurities in real time with accuracy. Outside fusion applications, Tthis technology makes it possible to detect also medical impurities in the human body (as cancer) or impurities in materials.
CeBr Scintillators

Technology, know-‐how, and expertise have been developed by a world-‐renowned nuclear fusion organization within the field of CeBr (Cerium Bromide) Scintillators. These scintillators have been characterized to have a fast response time of less than 20ns and the energy resolution at 511keV is about 4%. Previously, conventional gamma ray detectors have been unsatisfactory in their time resolution, limiting their applications in medical PET scanners and material science measurements.
Diamond Detector Matrix

A 12-‐pixels diamond based neutron spectrometer matrix has been built in a collaboration between the two CNR institutes IFP (Institute of Plasma Physics, Milan) and ISM (Institute of the Structure of Matter, Rome). The spectrometer is equipped with fast electronics and digital acquisition, which for the first time allows combined fast neutron spectroscopy (>1 MeV) with good energy resolution (<3% at 14 MeV) and high count-‐rate capability in excess of 1 MHz.
Axial Potential Separator suitable for Cryotechnics
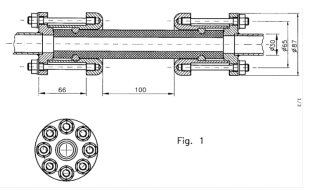
The technology innovation is a new electrical potential separator for cryotechnics. It is applicable particularly to electrically isolating areas, in which different potentials occur. The device consists of a dielectric tube e.g. made of polyimide, which still isolates when subjected to low temperatures as a result of its material properties. An annular groove is located on the exterior of both end areas of the tube, in which a support ring is inlaid. Electrodes are applied to the tube such that they cannot be removed. The electrodes themselves are detachably connected to flanges that are pulled onto the face of the tube to seal the device. The technology is ready for use in the non‐fusion domain and was patented by the inventors Stefan Fink and Günter Friesinger
Neutron-insensitive silicon ion detectors for NPA (Neutral Particle Analysis)
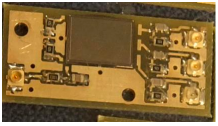
A leading European nuclear fusion institute has developed a thin silicon strip detector for 10‐1000 keV ions. The detector consists of an active silicon layer (5 µm thick for low‐energy ions, or 25 µm thick for detection of high-‐energy ions) bonded to a silicon support (~300 µm thick). Unlike previous ion detectors, the thin silicon strip detector exhibits high background‐to‐signal separation and good radiation tolerance, so is effective in high gamma, neutron, or photon backgrounds. The detector works by converting ion energy directly to charge in the silicon.
You did not find a technology that met your demand? Share your need !